
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a way to handle financial services, like borrowing, lending, or trading, without relying on traditional banks or financial institutions.
Instead, it uses blockchain technology (like Ethereum) to create a system where people can directly interact with each other to manage their money.
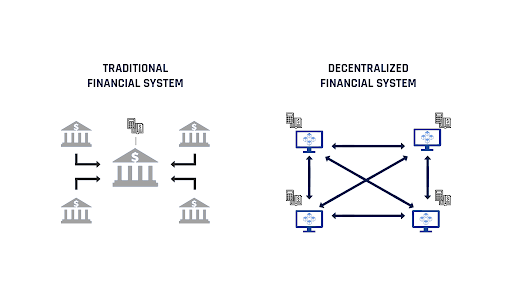
Here’s a simple way to understand DeFi:
Keep in mind that DeFi is still a relatively new concept, and while it has the potential to change the way we handle money, it also comes with risks. It’s essential to understand how it works and be cautious when using DeFi services.
Think of it like earning a company’s stock as you use its products.
Trust
Transparency
Identity and access
Returns
Risk
As you can see, DeFi has both advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional finance:
You can use DeFi to send money to others, earn yield on your assets, provide liquidity / loans to others, acquire loans yourself, and much more. Visit our DeFi learning path to dive in and learn more if you’re interested.
In our next section, we’ll cover: “What is an NFT?”
Learn more:
If you’re interested in building the future digital economy, we want to hear from you!